Page 19 - ICT Nepal News Issue 01
P. 19
(OCC) had initiated the digital signature. Even
works related to this the Government Root CA
under the Electronic has not been integrated
Transactions Act-2063 BS with Global CA and is not
and Regulations-2064 BS trusted in browsers as
with an objective of making Root CA, Nepal Root CA
electron ic tra nsactions is kept as Trusted Root
Secure and reliable. The CA manually in present
OCC has given permission internal context. DSC is
to Radiant lnfo-tech Nepal being implemented in
Company to issue digital Pu blic-Private Partnership
signatures. (PPP) model where still it
ln context of Nepal, lacks awareness. Special
PKI enabled application awareness programs
is not found in most should be conducted Digita I Signatu re Certifi cate
of the government for better information generators are not only
agencies. Many private about DS and relationship focusing on generating Using digital
as well as government between both public digital signature and
organizations i.e. banks and private sectors. certificate but also appeals sig natu re
and other business firms Government bodies all government bodies and
uses different a pplications like lnland Revenue individuals to use digital saves time,
like Pumori, Finacle, etc. Department (lRD), OCR, signatures to make "Digital
where DSC are not trusted Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) Nepal". money and
from the root which and other regulatory Apart from all the
doesn't makes even the bodies should help and problems and threats environment
top level of private as well initiate in the implication government bodies
as government agencies of DSC nationally. Nepal have been facing for
feel their ownership of Certifying Company, the implementing DSC
Encryption with Digital Signature
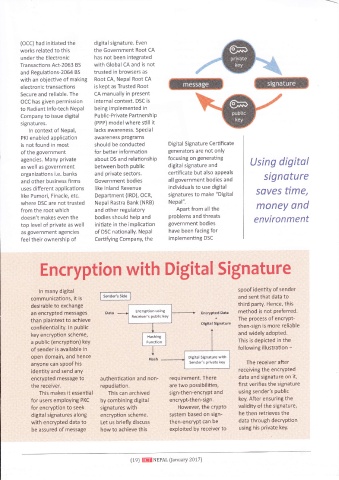
ln many digital spoof identity of sender
and sent that data to
communications, it is
desirable to exchange third party. Hence, this
Erxrwli*rt usiug method is not preferred.
an encrypted messages Encrypted Sata
gerewr:{s puhlic keY +
than plaintext to achieve The process of encryPt-
Digl,tal Sgnature
confi dentiality. ln public then-sign is more reliable
key encryption scheme, lla*\dr:q and widely adopted.
a public (encryption) key Funrl,i*n This is depicted in the
of sender is available in following illustration -
open domain, and hence *16;*al *ignalure with
anyone can spoof his Sendels prlvet* key The receiver after
identity and send any receiving the encrypted
encrypted message to authentication and non- requirement. There data and signature on it,
the receiver. repudiation. are two possibilities, first verifies the signature
This makes it essential This can archived sign-then-encrypt and using sender's public
for users employing PKC by combining digital encrypt-then-sign. key. After ensuring the
for encryption to seek signatures with Howeve6 the crYPto validity of the signature,
digital signatures along encryption scheme. system based on sign- he then retrieves the
with encrypted data to Let us briefly discuss then-encrypt can be data through decryPtion
be assured of message how to achieve this exploited by receiver to using his private key.
[19) IftI NEPAL (]anuary 201,7)