Page 15 - ICT Nepal News Issue 02
P. 15
and efficiently. Local beneficiaries is increasing
40000
e-government enables daily. 35000
administrations to The data of social 30m
extend services to local security beneficiaries 25m0
have been maintained 20000
communities by Providing
r5000
space and online means manually. Since the Process 10000
for people to get together is manual, there is high 5000
and communicate with chance of missing actual 0
each other and with beneficiaries and changes
local government. of ghost beneficiaries, who
Local authorities in may be benefitted twice
the developed world or more. The caPacitY
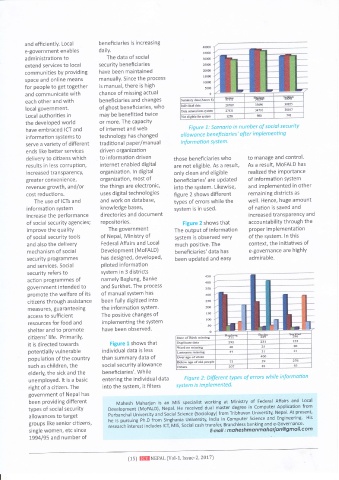
have embraced ICT and of internet and web Figure L: Scenorio in number of social security
information sYstems to technology has changed a I lowa nce be nefi cia ri es' ofte r i m ple me nti ng
serve a variety of different traditional paPer/ma nua I informotion sYstem.
ends like better services driven organization
delivery to citizens which to information driven those beneficiaries who to manage and control.
results in less corruPtion, internet enabled digital are not eligible. As a result, As a result, MoFALD has
i ncreased tra nspa rencY, organization. ln digital only clean and eligible realized the imPorta nce
greater convenience, organization, most of beneficiaries' are uPdated of information sYstem
revenue growth, and/or the things are electronic, into the system. Likewise, and implemented in other
cost reductions. uses digital technologies figure 2 shows different remaining districts as
The use of lCTs and and work on database, types of errors while the well. Hence, huge amount
information sYstem knowledge bases, system is in used. of nation is saved and
increase the performance directories and document increased transParencY and
of social securitY agencies; repositories. Figure 2 shows that accountabilitY through the
improve the qualitY The government The output of information proper implementation
of social security tools of Nepal, MinistrY of system is observed verY of the system. ln this
and also the deliverY Federal Affairs and Local much positive. The context, the initiatives of
mechanism of social Development (MoFALD) beneficiaries'data has e-governance are highlY
security programmes has designed, develoPed, been updated and easY admirable.
and services. Social piloted information
security refers to system in 3 districts
450
action programmes of namely Baglung, Banke 400
government intended to and Surkhet. The Process 350
promote the welfare of its of manual system has 300
citizens th rough assista nce been fully digitized into 250
measures, guaranteeing the information sYstem. 200
access to sufficient The positive changes of lso
too
resources for food and implementing the sYstem
50
shelter and to Promote have been observed. o
citizens' life. PrimarilY,
it is directed towards Figure 1 shows that
potentia I ly vu I nera ble individual data is less
population of the countrY than summary data of
such as children, the social security allowance
elderly, the sick and the beneficiaries'. While
unemployed. lt is a basic entering the individual data Figure 2: Different types of errors while informotion
right of a citizen. The into the system, it filters system is imPlemented.
government of NePal has
been providing different Mahesh Maharjan is an MIS specialist working at Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local
types of social securitY Development (MoFALD), Nepal. He received dual master degree in Computer Application from
purbanchal University and social Science (sociology) from Tribhuvan University, Nepal. At present,
allowances to target he is pursuing ph.D from Singhania University, tndia in Computer Science and Engineering' His
groups like senior citizens,
research interest includes lcT, Mls, social cash transfer, Branchless banking and e-Governance'
single women, etc since E-m o i t ; mohesh m o n mahorion@g moil'co m
1994/95 and number of
(15) Iff,INEPAL (Vol-1, Issue-Z, 201,7)